Sir Arthur Conan Doyle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character

 Doyle was born on 22 May 1859 at 11 Picardy Place,
Doyle was born on 22 May 1859 at 11 Picardy Place,
 Doyle was the doctor on the
Doyle was the doctor on the
Edinburgh Research Archive
. In 1882, Doyle partnered with his former classmate George Turnavine Budd in a medical practice in
 Doyle struggled to find a publisher. His first work featuring Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson, '' A Study in Scarlet'', was written in three weeks when he was 27 and was accepted for publication by
Doyle struggled to find a publisher. His first work featuring Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson, '' A Study in Scarlet'', was written in three weeks when he was 27 and was accepted for publication by  A sequel to ''A Study in Scarlet'' was commissioned, and '' The Sign of the Four'' appeared in '' Lippincott's Magazine'' in February 1890, under agreement with the Ward Lock company. Doyle felt grievously exploited by Ward Lock as an author new to the publishing world, and so, after this, he left them. Short stories featuring Sherlock Holmes were published in the ''
A sequel to ''A Study in Scarlet'' was commissioned, and '' The Sign of the Four'' appeared in '' Lippincott's Magazine'' in February 1890, under agreement with the Ward Lock company. Doyle felt grievously exploited by Ward Lock as an author new to the publishing world, and so, after this, he left them. Short stories featuring Sherlock Holmes were published in the '' In December 1893, to dedicate more of his time to his historical novels, Doyle had Holmes and
In December 1893, to dedicate more of his time to his historical novels, Doyle had Holmes and
 Doyle's first novels were '' The Mystery of Cloomber'', not published until 1888, and the unfinished '' Narrative of John Smith'', published only posthumously, in 2011. He amassed a portfolio of short stories, including "The Captain of the Pole-Star" and "J. Habakuk Jephson's Statement", both inspired by Doyle's time at sea. The latter popularised the mystery of the ''
Doyle's first novels were '' The Mystery of Cloomber'', not published until 1888, and the unfinished '' Narrative of John Smith'', published only posthumously, in 2011. He amassed a portfolio of short stories, including "The Captain of the Pole-Star" and "J. Habakuk Jephson's Statement", both inspired by Doyle's time at sea. The latter popularised the mystery of the ''
 In 1885 Doyle married Louisa (sometimes called "Touie") Hawkins (1857–1906). She was the youngest daughter of J. Hawkins, of Minsterworth, Gloucestershire, and the sister of one of Doyle's patients. Louisa had
In 1885 Doyle married Louisa (sometimes called "Touie") Hawkins (1857–1906). She was the youngest daughter of J. Hawkins, of Minsterworth, Gloucestershire, and the sister of one of Doyle's patients. Louisa had
 Doyle served as a volunteer physician in the Langman Field Hospital at
Doyle served as a volunteer physician in the Langman Field Hospital at
 Doyle was also a fervent advocate of justice and personally investigated two closed cases, which led to two men being exonerated of the crimes of which they were accused. The first case, in 1906, involved a shy half-British, half-Indian lawyer named
Doyle was also a fervent advocate of justice and personally investigated two closed cases, which led to two men being exonerated of the crimes of which they were accused. The first case, in 1906, involved a shy half-British, half-Indian lawyer named
 In 1919, the magician P. T. Selbit staged a séance at his flat in
In 1919, the magician P. T. Selbit staged a séance at his flat in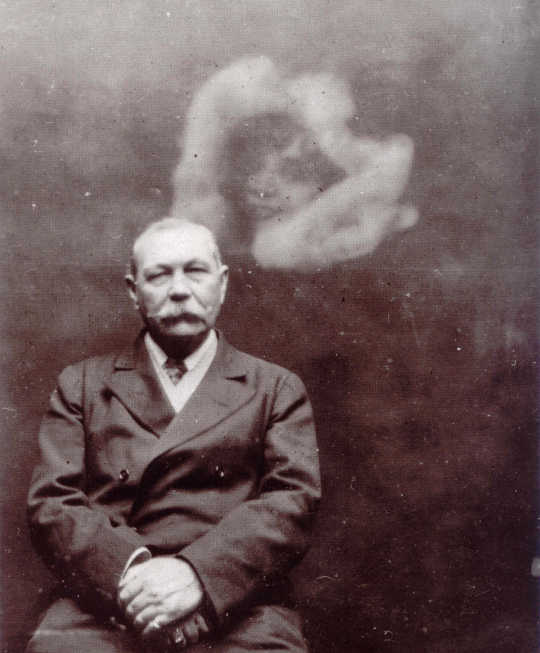  In 1922, the psychical researcher
In 1922, the psychical researcher
 Another of Doyle's longstanding interests was architectural design. In 1895, when he commissioned an architect friend of his, Joseph Henry Ball, to build him a home, he played an active part in the design process. The home in which he lived from October 1897 to September 1907, known as
Another of Doyle's longstanding interests was architectural design. In 1895, when he commissioned an architect friend of his, Joseph Henry Ball, to build him a home, he played an active part in the design process. The home in which he lived from October 1897 to September 1907, known as

 Doyle was found clutching his chest in the hall of Windlesham Manor, his house in
Doyle was found clutching his chest in the hall of Windlesham Manor, his house in

 Knight of Grace of the Most Venerable Order of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem (1903)
:
Knight of Grace of the Most Venerable Order of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem (1903)
:  Queen's South Africa Medal (1901)
:
Queen's South Africa Medal (1901)
:  Knight of the Order of the Crown of Italy (1895)
:
Knight of the Order of the Crown of Italy (1895)
:  Order of the Medjidie – 2nd Class (Ottoman Empire) (1907)
Order of the Medjidie – 2nd Class (Ottoman Empire) (1907)
''Debate on Spiritualism: Between Arthur Conan Doyle and Joseph McCabe''
The Appeal's Pocket Series. * Bernard M. L. Ernst, Hereward Carrington (1932). ''Houdini and Conan Doyle: The Story of a Strange Friendship''. Albert and Charles Boni, Inc. * Margalit Fox (2018). ''Conan Doyle for the Defense''. Random House. * Kelvin Jones (1989). ''Conan Doyle and the Spirits: The Spiritualist Career of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle''. Aquarian Press. * Jon Lellenberg, Daniel Stashower, Charles Foley (2007). ''Arthur Conan Doyle: A Life in Letters''. HarperPress. * Andrew Lycett (2008). ''The Man Who Created Sherlock Holmes: The Life and Times of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle''. Free Press. * Russell Miller (2008). ''The Adventures of Arthur Conan Doyle: A Biography''. Thomas Dunne Books. * Pierre Nordon (1967). ''Conan Doyle: A Biography''. Holt, Rinehart and Winston. * Ronald Pearsall (1977). ''Conan Doyle: A Biographical Solution''. Littlehampton Book Services Ltd. * Massimo Polidoro (2001). ''Final Séance: The Strange Friendship Between Houdini and Conan Doyle''. Prometheus Books. * Daniel Stashower (2000). ''Teller of Tales: The Life of Arthur Conan Doyle''. Penguin Books.
Works by Arthur Conan Doyle
at Project Gutenberg Australia * *
Poems by Arthur Conan Doyle
Physical collections
Arthur Conan Doyle PapersPhotographs
an
Personal Effects
at the Harry Ransom Center
Arthur Conan Doyle Collection
at Toronto Public Library
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle Collection
at Dartmouth College Library
*
at the Newberry Library * Biographical information
Doyle, Sir Arthur Conan, Knt. – Cr. 1902
''The county families of the United Kingdom'' or ''Royal manual of the titled and untitled aristocracy of England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland'', (Volume ed. 59, yr. 1919) (page 109 of 415) by Edward Walford
The Arthur Conan Doyle Encyclopedia
Conan Doyle in Birmingham
Other references
1930 audio recording of Conan Doyle speaking
* *
Arthur Conan Doyle quotes
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Doyle, Arthur Conan Arthur Conan Doyle, 1859 births 1930 deaths 19th-century British novelists 19th-century British short story writers 19th-century Scottish medical doctors 19th-century Scottish writers 19th-century male writers 20th-century British male writers 20th-century British novelists 20th-century Scottish medical doctors Alumni of the University of Edinburgh Association footballers not categorized by position British Freemasons British male boxers British children's writers British crime fiction writers British detective fiction writers British dramatists and playwrights British essayists British fantasy writers British historical novelists British horror writers British male novelists British male poets British memoirists British mystery writers British non-fiction writers British occult writers British opera librettists British people in whaling British people of Irish descent British science fiction writers British short story writers British spiritualists Deputy Lieutenants of Surrey Doyle family, Arthur Conan English footballers Former Roman Catholics Ghost story writers Knights Bachelor Knights of Grace of the Order of St John Legion of Frontiersmen members Liberal Unionist Party parliamentary candidates Male non-fiction writers Maritime writers Marylebone Cricket Club cricketers Mythopoeic writers People educated at Stonyhurst College People of the Second Boer War Recipients of the Order of the Crown (Italy) Scottish Christian mystics Scottish cricketers Sherlock Holmes Victorian novelists Writers from Edinburgh Writers of Gothic fiction Writers of historical fiction set in the Middle Ages Writers of historical fiction set in the modern age People of the National Rifle Association
Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a " consulting detective" in the stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with observation, deduction, forensic science and ...
in 1887 for '' A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Holmes and Dr. Watson. The Sherlock Holmes stories are milestones in the field of crime fiction
Crime fiction, detective story, murder mystery, mystery novel, and police novel are terms used to describe narratives that centre on criminal acts and especially on the investigation, either by an amateur or a professional detective, of a crime, ...
.
Doyle was a prolific writer; other than Holmes stories, his works include fantasy and science fiction stories about Professor Challenger and humorous stories about the Napoleonic soldier Brigadier Gerard, as well as plays, romances, poetry, non-fiction, and historical novels. One of Doyle's early short stories, "J. Habakuk Jephson's Statement
"J. Habakuk Jephson's Statement" is an 1884 short story by Arthur Conan Doyle. It is in the form of a first-person testimony by a survivor of the ''Marie Celeste'', a fictionalised version of the ''Mary Celeste'', a ship found mysteriously aband ...
" (1884), helped to popularise the mystery of the ''Mary Celeste
''Mary Celeste'' (; often erroneously referred to as Marie Celeste) was an American-registered merchant brigantine, best known for being discovered adrift and deserted in the Atlantic Ocean off the Azores Islands on December 4, 1872. The Cana ...
''.
Name
Doyle is often referred to as "Sir Arthur Conan Doyle" or "Conan Doyle", implying that "Conan" is part of a compound surname rather than a middle name. His baptism entry in the register of St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh, gives "Arthur Ignatius Conan" as his given names and "Doyle" as his surname. It also names Michael Conan as his godfather. The catalogues of theBritish Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom and is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the Briti ...
and the Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The libra ...
treat "Doyle" alone as his surname.
Steven Doyle, publisher of '' The Baker Street Journal'', wrote: "Conan was Arthur's middle name. Shortly after he graduated from high school he began using Conan as a sort of surname. But technically his last name is simply 'Doyle'." When knighted, he was gazetted as Doyle, not under the compound Conan Doyle.
Early life

 Doyle was born on 22 May 1859 at 11 Picardy Place,
Doyle was born on 22 May 1859 at 11 Picardy Place, Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
, Scotland. His father, Charles Altamont Doyle, was born in England, of Irish Catholic
Irish Catholics are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland whose members are both Catholic and Irish. They have a large diaspora, which includes over 36 million American citizens and over 14 million British citizens (a quarter of the Briti ...
descent, and his mother, Mary (née Foley), was Irish Catholic. His parents married in 1855. In 1864 the family scattered because of Charles's growing alcoholism, and the children were temporarily housed across Edinburgh. Arthur lodged with Mary Burton, the aunt of a friend, at Liberton Bank House on Gilmerton Road, while studying at Newington Academy.
In 1867, the family came together again and lived in squalid tenement flats at 3 Sciennes Place.Owen Dudley Edwards, "Doyle, Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan (1859–1930)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004. Doyle's father died in 1893, in the Crichton Royal, Dumfries
Dumfries ( ; sco, Dumfries; from gd, Dùn Phris ) is a market town and former royal burgh within the Dumfries and Galloway council area of Scotland. It is located near the mouth of the River Nith into the Solway Firth about by road from t ...
, after many years of psychiatric illness. Beginning at an early age, throughout his life Doyle wrote letters to his mother, and many of them were preserved.
Supported by wealthy uncles, Doyle was sent to England, to the Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
preparatory school Hodder Place, Stonyhurst in Lancashire, at the age of nine (1868–70). He then went on to Stonyhurst College
Stonyhurst College is a co-educational Roman Catholic independent school, adhering to the Jesuit tradition, on the Stonyhurst Estate, Lancashire, England. It occupies a Grade I listed building. The school has been fully co-educational sinc ...
, which he attended until 1875. While Doyle was not unhappy at Stonyhurst, he said he did not have any fond memories of it because the school was run on medieval principles: the only subjects covered were rudiments, rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate par ...
, Euclidean geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry: the '' Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms ...
, algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.
Elementary ...
and the classics. Doyle commented later in his life that this academic system could only be excused "on the plea that any exercise, however stupid in itself, forms a sort of mental dumbbell by which one can improve one's mind". He also found the school harsh, noting that, instead of compassion and warmth, it favoured the threat of corporal punishment and ritual humiliation.
From 1875 to 1876, he was educated at the Jesuit school Stella Matutina
The Stella Matutina (Morning Star) was an initiatory magical order dedicated to the dissemination of the traditional occult teachings of the earlier Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn. Originally, the outer order of the Stella Matutina was known a ...
in Feldkirch, Austria. His family decided that he would spend a year there in order to perfect his German and broaden his academic horizons. He later rejected the Catholic faith and became an agnostic
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficien ...
. One source attributed his drift away from religion to the time he spent in the less strict Austrian school. He also later became a spiritualist
Spiritualism is the metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spiritualism (when not lowercase) ...
mystic.
Medical career
From 1876 to 1881, Doyle studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh Medical School; during this period he spent time working inAston
Aston is an area of inner Birmingham, England. Located immediately to the north-east of Central Birmingham, Aston constitutes a ward within the metropolitan authority. It is approximately 1.5 miles from Birmingham City Centre.
History
Aston wa ...
(then a town in Warwickshire
Warwickshire (; abbreviated Warks) is a county in the West Midlands region of England. The county town is Warwick, and the largest town is Nuneaton. The county is famous for being the birthplace of William Shakespeare at Stratford-upon-Avo ...
, now part of Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
), Sheffield
Sheffield is a city in South Yorkshire, England, whose name derives from the River Sheaf which runs through it. The city serves as the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire ...
and Ruyton-XI-Towns, Shropshire. Also during this period, he studied practical botany at the Royal Botanic Garden in Edinburgh. While studying, Doyle began writing short stories. His earliest extant fiction, "The Haunted Grange of Goresthorpe", was unsuccessfully submitted to ''Blackwood's Magazine
''Blackwood's Magazine'' was a British magazine and miscellany printed between 1817 and 1980. It was founded by the publisher William Blackwood and was originally called the ''Edinburgh Monthly Magazine''. The first number appeared in April 1817 ...
''. His first published piece, " The Mystery of Sasassa Valley", a story set in South Africa, was printed in '' Chambers's Edinburgh Journal'' on 6 September 1879. On 20 September 1879, he published his first academic article, " Gelsemium as a Poison" in the ''British Medical Journal
''The BMJ'' is a weekly peer-reviewed medical trade journal, published by the trade union the British Medical Association (BMA). ''The BMJ'' has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Origi ...
'', a study which ''The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a national British daily broadsheet newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed across the United Kingdom and internationally.
It was f ...
'' regarded as potentially useful in a 21st-century murder investigation.
 Doyle was the doctor on the
Doyle was the doctor on the Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland ...
whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales.
Terminology
The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Japa ...
''Hope'' of Peterhead in 1880. On 11 July 1880, John Gray's ''Hope'' and David Gray's ''Eclipse'' met up with the ''Eira'' and Leigh Smith. The photographer W. J. A. Grant took a photograph aboard the ''Eira'' of Doyle along with Smith, the Gray brothers, and ship's surgeon William Neale, who were members of the Smith expedition. That expedition explored Franz Josef Land
, native_name =
, image_name = Map of Franz Josef Land-en.svg
, image_caption = Map of Franz Josef Land
, image_size =
, map_image = Franz Josef Land location-en.svg
, map_caption = Location of Franz Josef ...
, and led to the naming, on 18 August, of Cape Flora, Bell Island, Nightingale Sound, Gratton ("Uncle Joe") Island, and Mabel Island.
After graduating with Bachelor of Medicine and Master of Surgery (M.B. C.M.) degrees from the University of Edinburgh in 1881, he was ship's surgeon on the SS ''Mayumba'' during a voyage to the West African coast. He completed his Doctor of Medicine
Doctor of Medicine (abbreviated M.D., from the Latin ''Medicinae Doctor'') is a medical degree, the meaning of which varies between different jurisdictions. In the United States, and some other countries, the M.D. denotes a professional degree. ...
(M.D.) degree (an advanced degree beyond the basic medical qualification in the UK) with a dissertation on '' tabes dorsalis'' in 1885.Available at thEdinburgh Research Archive
. In 1882, Doyle partnered with his former classmate George Turnavine Budd in a medical practice in
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to ...
, but their relationship proved difficult, and Doyle soon left to set up an independent practice. Arriving in Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most d ...
in June 1882, with less than £10 (£ in ) to his name, he set up a medical practice at 1 Bush Villas in Elm Grove, Southsea
Southsea is a seaside resort and a geographic area of Portsmouth, Portsea Island in England. Southsea is located 1.8 miles (2.8 km) to the south of Portsmouth's inner city-centre. Southsea is not a separate town as all of Portsea Island's s ...
. The practice was not successful. While waiting for patients, Doyle returned to writing fiction.
Doyle was a staunch supporter of compulsory vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulat ...
and wrote several articles advocating the practice and denouncing the views of anti-vaccinators.
In early 1891, Doyle embarked on the study of ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a me ...
in Vienna. He had previously studied at the Portsmouth Eye Hospital in order to qualify to perform eye tests and prescribe glasses. Vienna had been suggested by his friend Vernon Morris as a place to spend six months and train to be an eye surgeon. But Doyle found it too difficult to understand the German medical terms being used in his classes in Vienna, and soon quit his studies there. For the rest of his two-month stay in Vienna, he pursued other activities, such as ice skating
Ice skating is the self-propulsion and gliding of a person across an ice surface, using metal-bladed ice skates. People skate for various reasons, including recreation (fun), exercise, competitive sports, and commuting. Ice skating may be per ...
with his wife Louisa and drinking with Brinsley Richards of the London ''Times''. He also wrote ''The Doings of Raffles Haw''.
After visiting Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
and Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
, he spent a few days in Paris observing Edmund Landolt, an expert on diseases of the eye. Within three months of his departure for Vienna, Doyle returned to London. He opened a small office and consulting room at 2 Upper Wimpole Street, or 2 Devonshire Place as it was then. (There is today a Westminster City Council
Westminster City Council is the local authority for the City of Westminster in Greater London, England. The city is divided into 20 wards, each electing three councillors. The council is currently composed of 31 Labour Party members and 23 Cons ...
commemorative plaque
A commemorative plaque, or simply plaque, or in other places referred to as a historical marker, historic marker, or historic plaque, is a plate of metal, ceramic, stone, wood, or other material, typically attached to a wall, stone, or other ...
over the front door.) He had no patients, according to his autobiography, and his efforts as an ophthalmologist were a failure.
Literary career
Sherlock Holmes
 Doyle struggled to find a publisher. His first work featuring Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson, '' A Study in Scarlet'', was written in three weeks when he was 27 and was accepted for publication by
Doyle struggled to find a publisher. His first work featuring Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson, '' A Study in Scarlet'', was written in three weeks when he was 27 and was accepted for publication by Ward Lock & Co
Ward, Lock & Co. was a publishing house in the United Kingdom that started as a partnership and developed until it was eventually absorbed into the publishing combine of Orion Publishing Group.
History
Ebenezer Ward and George Lock started a ...
on 20 November 1886, which gave Doyle £25 () in exchange for all rights to the story. The piece appeared a year later in the '' Beeton's Christmas Annual'' and received good reviews in ''The Scotsman
''The Scotsman'' is a Scottish compact newspaper and daily news website headquartered in Edinburgh. First established as a radical political paper in 1817, it began daily publication in 1855 and remained a broadsheet until August 2004. Its pare ...
'' and the ''Glasgow Herald
''The Herald'' is a Scottish broadsheet newspaper founded in 1783. ''The Herald'' is the longest running national newspaper in the world and is the eighth oldest daily paper in the world. The title was simplified from ''The Glasgow Herald'' in ...
''.
Holmes was partially modelled on Doyle's former university teacher Joseph Bell
Joseph Bell FRCSE (2 December 1837 – 4 October 1911) was a Scottish surgeon and lecturer at the medical school of the University of Edinburgh in the 19th century. He is best known as an inspiration for the literary character Sherlock Hol ...
. In 1892, in a letter to Bell, Doyle wrote, "It is most certainly to you that I owe Sherlock Holmes ... round the centre of deduction and inference and observation which I have heard you inculcate I have tried to build up a man", and in his 1924 autobiography, he remarked, "It is no wonder that after the study of such a character iz., BellI used and amplified his methods when in later life I tried to build up a scientific detective who solved cases on his own merits and not through the folly of the criminal." Robert Louis Stevenson
Robert Louis Stevenson (born Robert Lewis Balfour Stevenson; 13 November 1850 – 3 December 1894) was a Scottish novelist, essayist, poet and travel writer. He is best known for works such as '' Treasure Island'', ''Strange Case of Dr Jekyll ...
was able to recognise the strong similarity between Joseph Bell
Joseph Bell FRCSE (2 December 1837 – 4 October 1911) was a Scottish surgeon and lecturer at the medical school of the University of Edinburgh in the 19th century. He is best known as an inspiration for the literary character Sherlock Hol ...
and Sherlock Holmes: "My compliments on your very ingenious and very interesting adventures of Sherlock Holmes. ... can this be my old friend Joe Bell?" Other authors sometimes suggest additional influences—for instance, Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wid ...
's character C. Auguste Dupin, who is mentioned, disparagingly, by Holmes in ''A Study in Scarlet''. Dr. (John) Watson owes his surname, but not any other obvious characteristic, to a Portsmouth medical colleague of Doyle's, Dr. James Watson.
Strand Magazine
''The Strand Magazine'' was a monthly British magazine founded by George Newnes, composed of short fiction and general interest articles. It was published in the United Kingdom from January 1891 to March 1950, running to 711 issues, though th ...
''. Doyle wrote the first five Holmes short stories from his office at 2 Upper Wimpole Street (then known as Devonshire Place), which is now marked by a memorial plaque.
Doyle's attitude towards his most famous creation was ambivalent. In November 1891, he wrote to his mother: "I think of slaying Holmes, ... and winding him up for good and all. He takes my mind from better things." His mother responded, "You won't! You can't! You mustn't!" In an attempt to deflect publishers' demands for more Holmes stories, he raised his price to a level intended to discourage them, but found they were willing to pay even the large sums he asked. As a result, he became one of the best-paid authors of his time.
Professor Moriarty
Professor James Moriarty is a fictional character and criminal mastermind created by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle to be a formidable enemy for the author's fictional detective Sherlock Holmes. He was created primarily as a device by which Doyle coul ...
plunge to their deaths together down the Reichenbach Falls
The Reichenbach Falls (german: Reichenbachfälle) are a waterfall cascade of seven steps on the stream called Rychenbach in the Bernese Oberland region of Switzerland. They drop over a total height of about . At , the upper falls, known as t ...
in the story "The Final Problem
"The Final Problem" is a short story by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle featuring his detective character Sherlock Holmes. It was first published in ''The Strand Magazine'' in the United Kingdom, and '' McClure's'' in the United States, under the title ...
". Public outcry, however, led him to feature Holmes in 1901 in the novel ''The Hound of the Baskervilles
''The Hound of the Baskervilles'' is the third of the four crime novels by British writer Arthur Conan Doyle featuring the detective Sherlock Holmes. Originally serialised in ''The Strand Magazine'' from August 1901 to April 1902, it is set ...
''. Holmes's fictional connection with the Reichenbach Falls is celebrated in the nearby town of Meiringen
Meiringen () is a municipality in the Interlaken-Oberhasli administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. Besides the village of Meiringen, the municipality includes the settlements of Balm, Brünigen, Eisenbolgen, Hausen, Prasti, ...
.
In 1903, Doyle published his first Holmes short story in ten years, "The Adventure of the Empty House
"The Adventure of the Empty House", one of the 56 Sherlock Holmes short stories written by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, is one of 13 stories in the cycle collected as ''The Return of Sherlock Holmes''. It was first published in ''Collier's'' in the ...
", in which it was explained that only Moriarty had fallen, but since Holmes had other dangerous enemies—especially Colonel Sebastian Moran
Colonel Sebastian Moran is a fictional character in the stories written by Arthur Conan Doyle. An enemy of Sherlock Holmes, he first appears in the 1903 short story "The Adventure of the Empty House". Holmes once described him as "the second most ...
—he had arranged to make it look as if he too were dead. Holmes was ultimately featured in a total of 56 short stories
A short story is a piece of prose fiction that typically can be read in one sitting and focuses on a self-contained incident or series of linked incidents, with the intent of evoking a single effect or mood. The short story is one of the oldest t ...
—the last published in 1927—and four novels by Doyle, and has since appeared in many novels and stories by other authors.
Other works
Mary Celeste
''Mary Celeste'' (; often erroneously referred to as Marie Celeste) was an American-registered merchant brigantine, best known for being discovered adrift and deserted in the Atlantic Ocean off the Azores Islands on December 4, 1872. The Cana ...
'' Macdonald Hastings, ''Mary Celeste'', (1971); . and added fictional details such as that the ship was found in perfect condition (it had actually taken on water by the time it was discovered), and that its boats remained on board (the single boat was in fact missing). These fictional details have come to dominate popular accounts of the incident, and Doyle's alternative spelling of the ship's name as the ''Marie Celeste'' has become more commonly used than the original spelling.
Between 1888 and 1906, Doyle wrote seven historical novels, which he and many critics regarded as his best work. He also wrote nine other novels, and—later in his career (1912–29)—five narratives (two of novel length) featuring the irascible scientist Professor Challenger. The Challenger stories include his best-known work after the Holmes oeuvre, '' The Lost World''. His historical novels include ''The White Company
''The White Company'' is a historical adventure by British writer Arthur Conan Doyle, set during the Hundred Years' War. The story is set in England, France and Spain, in the years 1366 and 1367, against the background of the campaign of Edward ...
'' and its prequel
A prequel is a literary, dramatic or cinematic work whose story precedes that of a previous work, by focusing on events that occur before the original narrative. A prequel is a work that forms part of a backstory to the preceding work.
The term ...
''Sir Nigel
''Sir Nigel'' is a historical novel set during the early phase of the Hundred Years' War, spanning the years 1350 to 1356. It was written by British author Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, first published in serial form during 1905–06 where it was ill ...
'', set in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. He was a prolific author of short stories, including two collections set in Napoleonic times and featuring the French character Brigadier Gerard.
Doyle's works for the stage include ''Waterloo'', which centres on the reminiscences of an English veteran of the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
and features a character Gregory Brewster, written for Henry Irving
Sir Henry Irving (6 February 1838 – 13 October 1905), christened John Henry Brodribb, sometimes known as J. H. Irving, was an English stage actor in the Victorian era, known as an actor-manager because he took complete responsibility ...
; ''The House of Temperley'', the plot of which reflects his abiding interest in boxing; '' The Speckled Band'', adapted from his earlier short story "The Adventure of the Speckled Band
"The Adventure of the Speckled Band" is one of 56 short Sherlock Holmes stories written by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, the eighth story of twelve in the collection '' The Adventures of Sherlock Holmes''. It was originally published in ''Strand Mag ...
"; and an 1893 collaboration with J. M. Barrie on the libretto
A libretto (Italian for "booklet") is the text used in, or intended for, an extended musical work such as an opera, operetta, masque, oratorio, cantata or musical. The term ''libretto'' is also sometimes used to refer to the text of major li ...
of ''Jane Annie
''Jane Annie, or The Good Conduct Prize'' is a comic opera written in 1893 by J. M. Barrie and Arthur Conan Doyle, with music by Ernest Ford, a conductor and occasional composer.
When the Gilbert and Sullivan partnership disbanded after the pro ...
''.
Sporting career
While living inSouthsea
Southsea is a seaside resort and a geographic area of Portsmouth, Portsea Island in England. Southsea is located 1.8 miles (2.8 km) to the south of Portsmouth's inner city-centre. Southsea is not a separate town as all of Portsea Island's s ...
, the seaside resort of Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most d ...
, Doyle played football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
as a goalkeeper for Portsmouth Association Football Club, an amateur side, under the pseudonym A. C. Smith.
Doyle was a keen cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
er, and between 1899 and 1907 he played 10 first-class matches for the Marylebone Cricket Club
Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) is a cricket club founded in 1787 and based since 1814 at Lord's Cricket Ground, which it owns, in St John's Wood, London. The club was formerly the governing body of cricket retaining considerable global influe ...
(MCC). He also played for the amateur cricket teams the Allahakbarries and the Authors XI alongside fellow writers J. M. Barrie, P. G. Wodehouse and A. A. Milne. His highest score, in 1902 against London County, was 43. He was an occasional bowler who took one first-class wicket, W. G. Grace, and wrote a poem about the achievement.
In 1900, Doyle founded the Undershaw Rifle Club at his home, constructing a 100-yard range and providing shooting for local men, as the poor showing of British troops in the Boer War had led him to believe that the general population needed training in marksmanship. He was a champion of "miniature" rifle clubs, whose members shot small-calibre firearms on local ranges. These ranges were much cheaper and more accessible to working-class participants than large "fullbore" ranges, such as Bisley Camp Bisley may refer to:
;Places in England
* Bisley, Gloucestershire
* Bisley, Surrey
** National Shooting Centre, also known as Bisley Ranges, near the Surrey village
;Surname
* John Bisley (disambiguation)
*Simon Bisley
Simon Bisley is a Britis ...
, which were necessarily remote from population centres. Doyle went on to sit on the Rifle Clubs Committee of the National Rifle Association
The National Rifle Association of America (NRA) is a gun rights advocacy group based in the United States. Founded in 1871 to advance rifle marksmanship, the modern NRA has become a prominent gun rights lobbying organization while cont ...
.
In 1901, Doyle was one of three judges for the world's first major bodybuilding
Bodybuilding is the use of progressive resistance exercise to control and develop one's muscles (muscle building) by muscle hypertrophy for aesthetic purposes. It is distinct from similar activities such as powerlifting because it focuses ...
competition, which was organised by the "Father of Bodybuilding", Eugen Sandow
Eugen Sandow (born Friedrich Wilhelm Müller, ; 2 April 1867 – 14 October 1925) was a German bodybuilder and showman from Prussia. Born in Königsberg, Sandow became interested in bodybuilding at the age of ten during a visit to Italy. After a ...
. The event was held in London's Royal Albert Hall
The Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. One of the UK's most treasured and distinctive buildings, it is held in trust for the nation and managed by a registered charity which receives no govern ...
. The other two judges were the sculptor Sir Charles Lawes-Wittewronge and Eugen Sandow himself.
Doyle was an amateur boxer. In 1909, he was invited to referee the James Jeffries– Jack Johnson heavyweight championship fight in Reno, Nevada
Reno ( ) is a city in the northwest section of the U.S. state of Nevada, along the Nevada-California border, about north from Lake Tahoe, known as "The Biggest Little City in the World". Known for its casino and tourism industry, Reno is th ...
. Doyle wrote: "I was much inclined to accept ... though my friends pictured me as winding up with a revolver at one ear and a razor at the other. However, the distance and my engagements presented a final bar."
Also a keen golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping wi ...
er, Doyle was elected captain of the Crowborough Beacon Golf Club in Sussex
Sussex (), from the Old English (), is a historic county in South East England that was formerly an independent medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the Englis ...
for 1910. He had moved to Little Windlesham house in Crowborough
Crowborough is a town and civil parish in East Sussex, England, in the Weald at the edge of Ashdown Forest in the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, 7 miles (11 km) south-west of Royal Tunbridge Wells and 33 miles ( ...
with Jean Leckie, his second wife, and resided there with his family from 1907 until his death in July 1930.
He entered the English Amateur billiards
Cue sports are a wide variety of games of skill played with a cue, which is used to strike billiard balls and thereby cause them to move around a cloth-covered table bounded by elastic bumpers known as .
There are three major subdivisions ...
championship in 1913.
While living in Switzerland, Doyle became interested in skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee ( ...
, which was relatively unknown in Switzerland at the time. He wrote an article, "An Alpine Pass on 'Ski" for the December 1894 issue of '' The Strand Magazine'', in which he described his experiences with skiing and the beautiful alpine scenery that could be seen in the process. The article popularised the activity and began the long association between Switzerland and skiing.
Family life
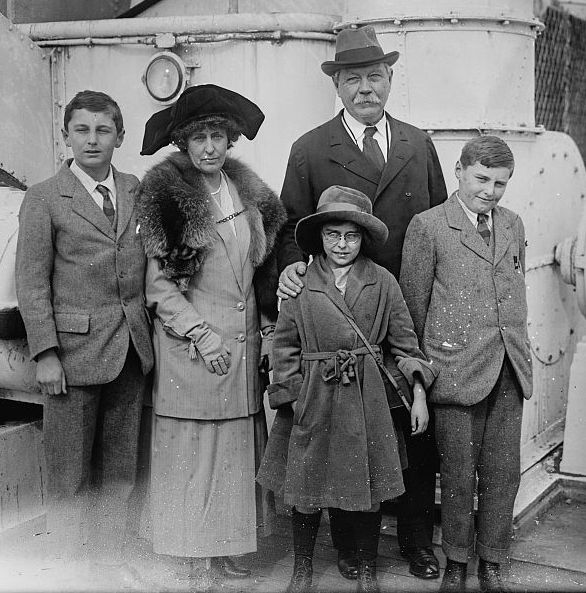
 In 1885 Doyle married Louisa (sometimes called "Touie") Hawkins (1857–1906). She was the youngest daughter of J. Hawkins, of Minsterworth, Gloucestershire, and the sister of one of Doyle's patients. Louisa had
In 1885 Doyle married Louisa (sometimes called "Touie") Hawkins (1857–1906). She was the youngest daughter of J. Hawkins, of Minsterworth, Gloucestershire, and the sister of one of Doyle's patients. Louisa had tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
.Leeman, Sue, "Sherlock Holmes fans hope to save Doyle's house from developers", Associated Press, 28 July 2006. In 1907, the year after Louisa's death, he married Jean Elizabeth Leckie (1874–1940). He had met and fallen in love with Jean in 1897, but had maintained a platonic relationship with her while his first wife was still alive, out of loyalty to her. Jean outlived him by ten years, and died in London.
Doyle fathered five children. He had two with his first wife: Mary Louise (1889–1976) and Arthur Alleyne Kingsley, known as Kingsley (1892–1918). He had an additional three with his second wife: Denis Percy Stewart (1909–1955), who became the second husband of Georgian Princess Nina Mdivani; Adrian Malcolm (1910–1970); and Jean Lena Annette (1912–1997). None of Doyle's five children had children of their own, so he has no living direct descendants.
Political campaigning
 Doyle served as a volunteer physician in the Langman Field Hospital at
Doyle served as a volunteer physician in the Langman Field Hospital at Bloemfontein
Bloemfontein, ( ; , "fountain of flowers") also known as Bloem, is one of South Africa's three capital cities and the capital of the Free State province. It serves as the country's judicial capital, along with legislative capital Cape To ...
between March and June 1900, during the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the So ...
in South Africa (1899–1902). Later that year, he wrote a book on the war, '' The Great Boer War'', as well as a short work titled ''The War in South Africa: Its Cause and Conduct'', in which he responded to critics of the United Kingdom's role in that war, and argued that its role was justified. The latter work was widely translated, and Doyle believed it was the reason he was knighted
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood finds origins in the G ...
(given the rank of Knight Bachelor
The title of Knight Bachelor is the basic rank granted to a man who has been knighted by the monarch but not inducted as a member of one of the organised orders of chivalry; it is a part of the British honours system. Knights Bachelor are ...
) by King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria an ...
in the 1902 Coronation Honours. He received the accolade from the King in person at Buckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a London royal residence and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and royal hospitality. It ...
on 24 October of that year.
He stood for Parliament twice as a Liberal Unionist
The Liberal Unionist Party was a British political party that was formed in 1886 by a faction that broke away from the Liberal Party. Led by Lord Hartington (later the Duke of Devonshire) and Joseph Chamberlain, the party established a politic ...
: in 1900 in Edinburgh Central; and in 1906 in the Hawick Burghs. He received a respectable share of the vote, but was not elected. He served as a Deputy-Lieutenant of Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant ur ...
beginning in 1902, and was appointed a Knight of Grace of the Order of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem in 1903.
Doyle was a supporter of the campaign for the reform of the Congo Free State
''(Work and Progress)
, national_anthem = Vers l'avenir
, capital = Vivi Boma
, currency = Congo Free State franc
, religion = Catholicism (''de facto'')
, leader1 = Leop ...
that was led by the journalist E. D. Morel and diplomat Roger Casement. In 1909 he wrote ''The Crime of the Congo
''The Crime of the Congo'' is a 1909 book by British writer and physician Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, about human rights abuses in the Congo Free State, a private state established and controlled by the King of the Belgians, Leopold II.
Synopsis
The ...
'', a long pamphlet in which he denounced the horrors of that colony. He became acquainted with Morel and Casement, and it is possible that, together with Bertram Fletcher Robinson, they inspired several characters that appear in his 1912 novel '' The Lost World''. Later, after the Irish Easter Rising
The Easter Rising ( ga, Éirí Amach na Cásca), also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week in April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans against British rule in Ireland with t ...
, Casement was found guilty of treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplo ...
against the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differ ...
, and was sentenced to death. Doyle tried, unsuccessfully, to save him, arguing that Casement had been driven mad, and therefore should not be held responsible for his actions.
As the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
loomed, and having been caught up in a growing public swell of Germanophobia, Doyle gave a public donation of 10 shillings to the anti-immigration British Brothers' League
The British Brothers' League (BBL) was a British anti-immigration, extraparliamentary, pressure group, the "largest and best organised" of its time. Described as proto-fascist, the group attempted to organise along paramilitary lines.
History
...
. In 1914, Doyle was one of fifty-three leading British authors—including H. G. Wells, Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)'' The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
and Thomas Hardy
Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Wor ...
—who signed their names to the "Authors' Declaration", justifying Britain’s involvement in the First World War. This manifesto declared that the German invasion of Belgium had been a brutal crime, and that Britain "could not without dishonour have refused to take part in the present war".
Legal advocate
 Doyle was also a fervent advocate of justice and personally investigated two closed cases, which led to two men being exonerated of the crimes of which they were accused. The first case, in 1906, involved a shy half-British, half-Indian lawyer named
Doyle was also a fervent advocate of justice and personally investigated two closed cases, which led to two men being exonerated of the crimes of which they were accused. The first case, in 1906, involved a shy half-British, half-Indian lawyer named George Edalji
George Ernest Thompson Edalji (22 January 1876 – 17 June 1953) was an English solicitor and son of a vicar of Parsi descent in a Staffordshire village. He became known as a victim of a miscarriage of justice for having served three year ...
, who had allegedly penned threatening letters and mutilated animals in Great Wyrley. Police were set on Edalji's conviction, even though the mutilations continued after their suspect was jailed. Apart from helping George Edalji, Doyle's work helped establish a way to correct other miscarriages of justice, as it was partially as a result of this case that the Court of Criminal Appeal was established in 1907.
The story of Doyle and Edalji was dramatised in an episode of the 1972 BBC television series, ''The Edwardians''. In Nicholas Meyer's pastiche '' The West End Horror'' (1976), Holmes manages to help clear the name of a shy Parsi
Parsis () or Parsees are an ethnoreligious group of the Indian subcontinent adhering to Zoroastrianism. They are descended from Persians who migrated to Medieval India during and after the Arab conquest of Iran (part of the early Muslim conq ...
Indian character wronged by the English justice system. Edalji was of Parsi heritage on his father's side. The story was fictionalised in Julian Barnes
Julian Patrick Barnes (born 19 January 1946) is an English writer. He won the Man Booker Prize in 2011 with ''The Sense of an Ending'', having been shortlisted three times previously with '' Flaubert's Parrot'', '' England, England'', and ''Art ...
's 2005 novel '' Arthur and George'', which was adapted into a three-part drama by ITV in 2015.
The second case, that of Oscar Slater
Oscar Joseph Slater (8 January 1872 – 31 January 1948) was the victim of a miscarriage of justice in Scotland. Wrongly convicted of murder and sentenced to death, he was freed after almost two decades of hard labour at Scotland’s HM Priso ...
—a Jew of German origin who operated a gambling den and was convicted of bludgeoning an 82-year-old woman in Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popu ...
in 1908—excited Doyle's curiosity because of inconsistencies in the prosecution's case and a general sense that Slater was not guilty. He ended up paying most of the costs for Slater's successful 1928 appeal.
Freemasonry and spiritualism
Doyle had a longstanding interest inmystical
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute, but may refer to any kind of ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in u ...
subjects and remained fascinated by the idea of paranormal
Paranormal events are purported phenomena described in popular culture, folk, and other non-scientific bodies of knowledge, whose existence within these contexts is described as being beyond the scope of normal scientific understanding. Not ...
phenomena, even though the strength of his belief in their reality waxed and waned periodically over the years.
In 1887, in Southsea, influenced by Major-General Alfred Wilks Drayson
Alfred Wilks Drayson (also Wilkes) (1827–1901) was an English army officer, author and astronomer. He was a personal friend of Arthur Conan Doyle, who dedicated to him the short story collection ''The Captain of the Polestar''.
Background
Born 1 ...
, a member of the Portsmouth Literary and Philosophical Society, Doyle began a series of investigations into the possibility of psychic phenomena and attended about 20 seances, experiments in telepathy
Telepathy () is the purported vicarious transmission of information from one person's mind to another's without using any known human sensory channels or physical interaction. The term was first coined in 1882 by the classical scholar Frederic ...
, and sittings with mediums. Writing to spiritualist
Spiritualism is the metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spiritualism (when not lowercase) ...
journal ''Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 t ...
'' that year, he declared himself to be a spiritualist, describing one particular event that had convinced him psychic phenomena were real. Also in 1887 (on 26 January), he was initiated as a Freemason
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
at the Phoenix Lodge No. 257 in Southsea. (He resigned from the Lodge in 1889, returned to it in 1902, and resigned again in 1911.)
In 1889, he became a founding member of the Hampshire Society for Psychical Research; in 1893, he joined the London-based Society for Psychical Research
The Society for Psychical Research (SPR) is a nonprofit organisation in the United Kingdom. Its stated purpose is to understand events and abilities commonly described as psychic or paranormal. It describes itself as the "first society to co ...
; and in 1894, he collaborated with Sir Sidney Scott and Frank Podmore in a search for poltergeists in Devon.
Doyle and the spiritualist William Thomas Stead
William Thomas Stead (5 July 184915 April 1912) was a British newspaper editor who, as a pioneer of investigative journalism, became a controversial figure of the Victorian era. Stead published a series of hugely influential campaigns whilst e ...
(before the latter was lost in the sinking of the ''Titanic'') were led to believe that Julius and Agnes Zancig
Julius and Agnes Zancig were stage magicians and authors on occultism who performed a spectacularly successful two-person mentalism act during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Julius Zancig (1857–1929) – born Julius Jörgensen in Copen ...
had genuine psychic powers, and they claimed publicly that the Zancigs used telepathy
Telepathy () is the purported vicarious transmission of information from one person's mind to another's without using any known human sensory channels or physical interaction. The term was first coined in 1882 by the classical scholar Frederic ...
. However, in 1924, the Zancigs confessed that their mind reading act had been a trick; they published the secret code and all other details of the trick method they had used under the title "Our Secrets!!" in a London newspaper. Doyle also praised the psychic
A psychic is a person who claims to use extrasensory perception (ESP) to identify information hidden from the normal senses, particularly involving telepathy or clairvoyance, or who performs acts that are apparently inexplicable by natural laws ...
phenomena and spirit materialisations that he believed had been produced by Eusapia Palladino
Eusapia Palladino (alternative spelling: ''Paladino''; 21 January 1854 – 16 May 1918) was an Italian Spiritualist physical medium. She claimed extraordinary powers such as the ability to levitate tables, communicate with the dead through ...
and Mina Crandon
Mina "Margery" Crandon (1888–November 1, 1941) was a psychical medium who claimed that she channeled her dead brother, Walter Stinson. Investigators who studied Crandon concluded that she had no such paranormal ability, and others detected her ...
, both of whom were also later exposed as frauds.William Kalush, Larry Ratso Sloman. (2006). ''The Secret Life of Houdini: The Making of America's First Superhero''. Atria Books. .
In 1916, at the height of the First World War, Doyle's belief in psychic phenomena was strengthened by what he took to be the psychic abilities of his children's nanny, Lily Loder Symonds. This and the constant drumbeat of wartime deaths inspired him with the idea that spiritualism was what he called a "New Revelation" sent by God to bring solace to the bereaved. He wrote a piece in ''Light'' magazine about his faith and began lecturing frequently on spiritualism. In 1918, he published his first spiritualist work, ''The New Revelation''.
Some have mistakenly assumed that Doyle's turn to spiritualism was prompted by the death of his son Kingsley, but Doyle began presenting himself publicly as a spiritualist in 1916, and Kingsley died on 28 October 1918 (from pneumonia contracted during his convalescence after being seriously wounded in the 1916 Battle of the Somme
The Battle of the Somme (French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place be ...
). Nevertheless, the war-related deaths of many people who were close to him appears to have even further strengthened his long-held belief in life after death and spirit communication. Doyle's brother Brigadier-general
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed t ...
Innes Doyle died, also from pneumonia, in February 1919. His two brothers-in-law (one of whom was E. W. Hornung, creator of the literary character Raffles), as well as his two nephews, also died shortly after the war. His second book on spiritualism, '' The Vital Message'', appeared in 1919.
Doyle found solace in supporting spiritualism's ideas and the attempts of spiritualists to find proof of an existence beyond the grave. In particular, according to some, he favoured Christian Spiritualism
Spiritualism is a metaphysical belief that the world is made up of at least two fundamental substances, matter and spirit. This very broad metaphysical distinction is further developed into many and various forms by the inclusion of details ab ...
and encouraged the Spiritualists' National Union
The Spiritualists' National Union (SNU) is a Spiritualist organisation, founded in the United Kingdom in 1901, and is one of the largest Spiritualist groups in the world. Its motto is ''Light, Nature, Truth''.
Over its history, it has organised t ...
to accept an eighth precept – that of following the teachings and example of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
. He was a member of the renowned supernaturalist organisation The Ghost Club
The Ghost Club is a paranormal investigation and research organization, founded in London in 1862. It is believed to be the oldest such organization in the world, though its history has not been continuous. The club still investigates mainly gho ...
.
 In 1919, the magician P. T. Selbit staged a séance at his flat in
In 1919, the magician P. T. Selbit staged a séance at his flat in Bloomsbury
Bloomsbury is a district in the West End of London. It is considered a fashionable residential area, and is the location of numerous cultural, intellectual, and educational institutions.
Bloomsbury is home of the British Museum, the largest ...
, which Doyle attended. Although some later claimed that Doyle had endorsed the apparent instances of clairvoyance at that séance as genuine, a contemporaneous report by the '' Sunday Express'' quoted Doyle as saying "I should have to see it again before passing a definite opinion on it" and "I have my doubts about the whole thing". In 1920, Doyle and the noted sceptic Joseph McCabe held a public debate at Queen's Hall in London, with Doyle taking the position that the claims of spiritualism
Spiritualism is the metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spiritualism (when not lowercase ...
were true. After the debate, McCabe published a booklet ''Is Spiritualism Based on Fraud?'', in which he laid out evidence refuting Doyle's arguments and claimed that Doyle had been duped into believing in spiritualism through deliberate mediumship
Mediumship is the practice of purportedly mediating communication between familiar spirits or spirits of the dead and living human beings. Practitioners are known as "mediums" or "spirit mediums". There are different types of mediumship or spir ...
trickery.
Doyle also debated the psychiatrist Harold Dearden, who vehemently disagreed with Doyle's belief that many cases of diagnosed mental illness
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitt ...
were the result of spirit possession
Spirit possession is an unusual or altered state of consciousness and associated behaviors purportedly caused by the control of a human body by spirits, ghosts, demons, or gods. The concept of spirit possession exists in many cultures and re ...
.
In 1920, Doyle travelled to Australia and New Zealand on spiritualist missionary work, and over the next several years, until his death, he continued his mission, giving talks about his spiritualist conviction in Britain, Europe, and the United States.
Doyle wrote a novel ''The Land of Mist
''The Land of Mist'' is a novel by British writer Arthur Conan Doyle, published in 1926.
Although this is a Professor Challenger story, it centres more on his daughter Enid and his old friend Edward Malone. Another friend from the 1912 novel ...
'' centred on spiritualist themes and featuring the character Professor Challenger. He also wrote many non-fiction spiritualist works. Perhaps his most famous of these was ''The Coming of the Fairies'' (1922), in which Doyle described his beliefs about the nature and existence of fairies and spirits, reproduced the five Cottingley Fairies photographs, asserted that those who suspected them being faked were wrong, and expressed his conviction that they were authentic. Decades later, the photos—taken by cousins Frances Griffiths and Elsie Wright—were definitively shown to have been faked, and their creators admitted to the fakery, although both maintained that they really had seen fairies.
Doyle was friends for a time with the American magician Harry Houdini. Even though Houdini explained that his feats were based on illusion and trickery, Doyle was convinced that Houdini had supernatural powers and said as much in his work ''The Edge of the Unknown''. Houdini's friend Bernard M. L. Ernst recounted a time when Houdini had performed an impressive trick at his home in Doyle's presence. Houdini had assured Doyle that the trick was pure illusion and had expressed the hope that this demonstration would persuade Doyle not to go around "endorsing phenomena" simply because he could think of no explanation for what he had seen other than supernatural power. However, according to Ernst, Doyle simply refused to believe that it had been a trick. Houdini became a prominent opponent of the spiritualist movement in the 1920s, after the death of his beloved mother. He insisted that spiritualist mediums employed trickery, and consistently exposed them as frauds. These differences between Houdini and Doyle eventually led to a bitter, public falling-out between them.
 In 1922, the psychical researcher
In 1922, the psychical researcher Harry Price
Harry Price (17 January 1881 – 29 March 1948) was a British psychic researcher and author, who gained public prominence for his investigations into psychical phenomena and exposing fraudulent spiritualist mediums. He is best known for ...
accused the "spirit photographer" William Hope of fraud. Doyle defended Hope, but further evidence of trickery was obtained from other researchers. Doyle threatened to have Price evicted from the National Laboratory of Psychical Research
The National Laboratory of Psychical Research was established in 1926 by Harry Price, at 16 Queensberry Place, London. Its aim was "to investigate in a dispassionate manner and by purely scientific means every phase of psychic or alleged psychic ...
and predicted that, if he persisted in writing what he called "sewage" about spiritualists, he would meet the same fate as Harry Houdini. Price wrote: "Arthur Conan Doyle and his friends abused me for years for exposing Hope." In response to the exposure of frauds that had been perpetrated by Hope and other spiritualists, Doyle led 84 members of the Society for Psychical Research
The Society for Psychical Research (SPR) is a nonprofit organisation in the United Kingdom. Its stated purpose is to understand events and abilities commonly described as psychic or paranormal. It describes itself as the "first society to co ...
to resign in protest from the society on the ground that they believed it was opposed to spiritualism.
Doyle's two-volume book ''The History of Spiritualism'' was published in 1926. W. Leslie Curnow, a spiritualist, contributed much research to the book. Later that year, Robert John Tillyard
Robert "Robin" John Tillyard FRS (31 January 1881 – 13 January 1937) was an English–Australian entomologist and geologist.
Early life and education
Tillyard was the son of J. J. Tillyard and his wife Mary Ann Frances, née Wilson and was ...
wrote a predominantly supportive review of it in the journal ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physics, physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. ...
''. This review provoked controversy: Several other critics, notably A. A. Campbell Swinton, pointed out the evidence of fraud in mediumship, as well as Doyle's non-scientific approach to the subject. In 1927, Doyle gave a filmed interview, in which he spoke about Sherlock Holmes and spiritualism.
Doyle and the Piltdown Hoax
Richard Milner, an American historian of science, argued that Doyle may have been the perpetrator of thePiltdown Man
The Piltdown Man was a paleoanthropological fraud in which bone fragments were presented as the fossilised remains of a previously unknown early human. Although there were doubts about its authenticity virtually from the beginning, the remains ...
hoax of 1912, creating the counterfeit hominid fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
that fooled the scientific world for over 40 years. Milner noted that Doyle had a plausible motive—namely, revenge on the scientific establishment for debunking one of his favourite psychics—and said that ''The Lost World'' appeared to contain several clues referring cryptically to his having been involved in the hoax. Samuel Rosenberg's 1974 book '' Naked is the Best Disguise'' purports to explain how, throughout his writings, Doyle had provided overt clues to otherwise hidden or suppressed aspects of his way of thinking that seemed to support the idea that Doyle would be involved in such a hoax.
However, more recent research suggests that Doyle was not involved. In 2016, researchers at the Natural History Museum
A natural history museum or museum of natural history is a scientific institution with natural history collections that include current and historical records of animals, plants, fungi, ecosystems, geology, paleontology, climatology, and more. ...
and Liverpool John Moores University analyzed DNA evidence showing that responsibility for the hoax lay with the amateur archaeologist Charles Dawson, who had originally "found" the remains. He had initially not been considered the likely perpetrator, because the hoax was seen as being too elaborate for him to have devised. However, the DNA evidence showed that a supposedly ancient tooth he had "discovered" in 1915 (at a different site) came from the same jaw as that of the Piltdown Man, suggesting that he had planted them both. That tooth, too, was later proven to have been planted as part of a hoax.
Chris Stringer, an anthropologist from the Natural History Museum, was quoted as saying: "Conan Doyle was known to play golf at the Piltdown site and had even given Dawson a lift in his car to the area, but he was a public man and very busy and it is very unlikely that he would have had the time o create the hoax So there are some coincidences, but I think they are just coincidences. When you look at the fossil evidence you can only associate Dawson with all the finds, and Dawson was known to be personally ambitious. He wanted professional recognition. He wanted to be a member of the Royal Society and he was after an MBE ic He wanted people to stop seeing him as an amateur".
Architecture
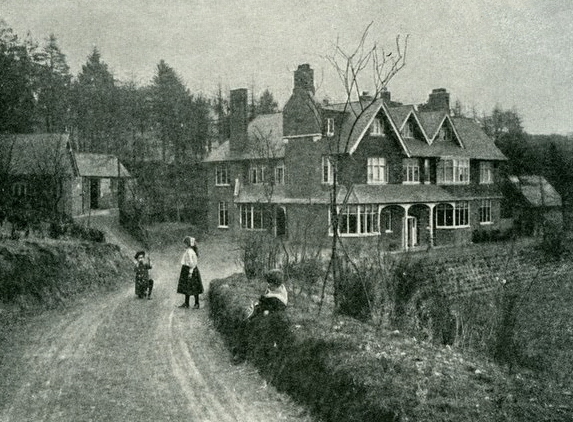
 Another of Doyle's longstanding interests was architectural design. In 1895, when he commissioned an architect friend of his, Joseph Henry Ball, to build him a home, he played an active part in the design process. The home in which he lived from October 1897 to September 1907, known as
Another of Doyle's longstanding interests was architectural design. In 1895, when he commissioned an architect friend of his, Joseph Henry Ball, to build him a home, he played an active part in the design process. The home in which he lived from October 1897 to September 1907, known as Undershaw
Undershaw is a former residence of the author Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, the creator of Sherlock Holmes. The house was built for Doyle at his order to accommodate his wife's health requirements, and is where he lived with his family from 1897 to 19 ...
(near Hindhead
Hindhead is a village in Surrey, England. It is the highest village in Surrey, with buildings at between 185 and 253 metres above sea level. It is best known as the location of the Devil's Punch Bowl, a beauty spot and site of special scienti ...
, in Surrey), was used as a hotel and restaurant from 1924 until 2004, when it was bought by a developer and then stood empty while conservationists and Doyle fans fought to preserve it. In 2012, the High Court in London ruled in favor of those seeking to preserve the historic building, ordering that the redevelopment permission be quashed on the ground that it had not been obtained through proper procedures. The building was later approved to become part of Stepping Stones, a school for children with disabilities and special needs.
Doyle made his most ambitious foray into architecture in March 1912, while he was staying at the Lyndhurst Grand Hotel: He sketched the original designs for a third-storey extension and for an alteration of the front facade of the building. Work began later that year, and when it was finished, the building was a nearly exact manifestation of the plans Doyle had sketched. Superficial alterations have been subsequently made, but the essential structure is still clearly Doyle's.
In 1914, on a family trip to the Jasper National Park in Canada, he designed a golf course and ancillary buildings for a hotel. The plans were realised in full, but neither the golf course nor the buildings have survived.
In 1926, Doyle laid the foundation stone for a Spiritualist Temple in Camden, London. Of the building's total £600 construction costs, he provided £500.
Crimes Club
The Crimes Club was a private social club founded by Doyle in 1903, whose purpose was discussion of crime and detection, criminals and criminology, and continues to this day as "Our Society", with membership numbers limited to 100. The club meets four times a year at the Imperial Hotel, Russell Square, London, where all proceedings are strictly confidential ("Chatham House rules
Under the Chatham House Rule, anyone who comes to a meeting is free to use information from the discussion, but is not allowed to reveal who made any particular comment. It is designed to increase openness of discussion. The rule is a system for h ...
"). Its logo is a silhouette of Doyle.
The club's earliest members included John Churton Collins
John Churton Collins (26 March 1848 – 25 September 1908) was a British literary critic.
Biography
Churton Collins was born at Bourton-on-the-Water, Gloucestershire, England. From King Edward's School, Birmingham, he went to Balliol College, ...
, Japanologist Arthur Diósy, Sir Edward Marshall Hall
Sir Edward Marshall Hall, (16 September 1858 – 24 February 1927) was an English barrister who had a formidable reputation as an orator. He successfully defended many people accused of notorious murders and became known as "The Great Defende ...
, Sir Travers Humphreys
Sir Richard Somers Travers Christmas Humphreys (4 August 1867 – 20 February 1956) was a noted British barrister and judge who, during a sixty-year legal career, was involved in the cases of Oscar Wilde and the murderers Hawley Harvey Crippen, ...
, H. B. Irving
Harry Brodribb Irving (5 August 1870 – 17 October 1919), was a British stage actor and actor-manager; the eldest son of Sir Henry Irving and his wife Florence ( née O'Callaghan), and father of designer Laurence Irving and actress Elizabeth ...
, author (''Thou Shalt Do No Murder'') Arthur Lambton, William Le Queux
William Tufnell Le Queux ( , ; 2 July 1864 – 13 October 1927) was an Anglo-French journalist and writer. He was also a diplomat (honorary consul for San Marino), a traveller (in Europe, the Balkans and North Africa), a flying buff who officia ...
, A. E. W. Mason, coroner Ingleby Oddie, Sir Max Pemberton
Sir Max Pemberton (19 June 1863 – 22 February 1950) was a popular English novelist, working mainly in the adventure and mystery genres.LeRoy Lad Panek, ''After Sherlock Holmes: The Evolution of British and American Detective Stories, 1891– ...
, Bertram Fletcher Robinson, George R. Sims
George Robert Sims (2 September 1847 – 4 September 1922) was an English journalist, poet, dramatist, novelist and ''bon vivant''.
Sims began writing lively humour and satiric pieces for ''Fun'' magazine and ''The Referee'', but he was soon co ...
, Sir Bernard Spilsbury
Sir Bernard Henry Spilsbury (16 May 1877 – 17 December 1947) was a British pathologist. His cases include Hawley Crippen, the Seddon case, the Major Armstrong poisoning, the "Brides in the Bath" murders by George Joseph Smith, the Crumbles ...
, P. G. Wodehouse
Sir Pelham Grenville Wodehouse, ( ; 15 October 188114 February 1975) was an English author and one of the most widely read humorists of the 20th century. His creations include the feather-brained Bertie Wooster and his sagacious valet, Jeeve ...
, and Filson Young
Alexander Bell Filson Young (1876–1938) was a journalist, who published the first book about the sinking of the ''RMS Titanic'', called ''Titanic'', in 1912 only 37 days after the sinking. He was also an essayist, war correspondent in the Boer W ...
.
Death

 Doyle was found clutching his chest in the hall of Windlesham Manor, his house in
Doyle was found clutching his chest in the hall of Windlesham Manor, his house in Crowborough
Crowborough is a town and civil parish in East Sussex, England, in the Weald at the edge of Ashdown Forest in the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, 7 miles (11 km) south-west of Royal Tunbridge Wells and 33 miles ( ...
, Sussex, on 7 July 1930. He died of a heart attack at the age of 71. His last words were directed toward his wife: "You are wonderful." At the time of his death, there was some controversy concerning his burial place, as he was avowedly not a Christian, considering himself a Spiritualism, Spiritualist. He was first buried on 11 July 1930 in Windlesham rose garden.
He was later reinterred together with his wife in Minstead churchyard in the New Forest, Hampshire. Carved wooden tablets to his memory and to the memory of his wife, originally from the church at Minstead, are on display as part of a Sherlock Holmes exhibition at Portsmouth Museum. The epitaph on his gravestone in the churchyard reads, in part: "Steel true/Blade straight/Arthur Conan Doyle/Knight/Patriot, Physician and man of letters".
A statue honours Doyle at Crowborough Cross in Crowborough, where he lived for 23 years. There is a statue of Sherlock Holmes in Picardy Place, Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
, close to the house where Doyle was born.
Honours and awards
:
Knight Bachelor
The title of Knight Bachelor is the basic rank granted to a man who has been knighted by the monarch but not inducted as a member of one of the organised orders of chivalry; it is a part of the British honours system. Knights Bachelor are ...
(1902)
:  Order of the Medjidie – 2nd Class (Ottoman Empire) (1907)
Order of the Medjidie – 2nd Class (Ottoman Empire) (1907)
Commemoration
Doyle has been commemorated with statues and plaques since his death. In 2009, he was among the ten people selected by the Royal Mail for their Great Britain commemorative stamps 2000–2009, "Eminent Britons" commemorative postage stamp issue.Portrayals
Arthur Conan Doyle has been portrayed by many actors, including:Television series
*Nigel Davenport in the BBC Two series ''The Edwardians (miniseries), The Edwardians'', in the episode "Conan Doyle" (1972) *Michael Ensign in the ''Voyagers!'' episode "Jack's Back" (1983) *Robin Laing and Charles Edwards (English actor), Charles Edwards in ''Murder Rooms: Mysteries of the Real Sherlock Holmes'' (2000–2001) *Geraint Wyn Davies in ''Murdoch Mysteries'', 3 episodes (2008–2013) *Alfred Molina in the ''Drunk History'' (American series) episode "Detroit" (2013) *David Calder (actor), David Calder in the miniseries ''Houdini (miniseries), Houdini'' (2014) *Martin Clunes in the miniseries ''Arthur & George (TV series), Arthur & George'' (2015) *Bruce Mackinnon and Bradley Walsh in ''Drunk History (British TV series), Drunk History'' (British series), in series 2, episodes 5 and 8 respectively (2016) *Stephen Mangan in ''Houdini & Doyle'' (2016) *Michael Pitthan in the German TV series ''Charité (TV series), Charité'' episode "Götterdämmerung" (2017) *Bill Paterson (actor), Bill Paterson in the ''Urban Myths'' episode "Agatha Christie" (2018)Television films
*Peter Cushing in ''The Great Houdini (film), The Great Houdini'' (1976) *David Warner (actor), David Warner in ''Houdini (1998 film), Houdini'' (1998) *Richard Wilson (Scottish actor), Richard Wilson in ''Reichenbach Falls (film), Reichenbach Falls'' (2007) *Michael McElhatton in ''Agatha and the Truth of Murder'' (2018)Theatrical films
*Paul Bildt in ''The Man Who Was Sherlock Holmes'' (1937) *Peter O'Toole in ''FairyTale: A True Story'' (1997) *Edward Hardwicke in ''Photographing Fairies'' (1997) *Tom Fisher (actor), Tom Fisher in ''Shanghai Knights'' (2003) *Ian Hart in ''Finding Neverland (film), Finding Neverland'' (2004)Other media
*Carleton Hobbs in the BBC radio drama ''Conan Doyle Investigates'' (1972) *Iain Cuthbertson in the BBC radio drama ''Conan Doyle and The Edalji Case'' (1987) *Peter Jeffrey in the BBC radio drama ''Conan Doyle's Strangest Case'' (1995) *Adrian Lukis in the stage adaptation of the novel ''Arthur & George'' (2010) *Chris Tallman in Chapter 10 of ''The Dead Authors Podcast'' (2012) *Steven Miller (actor), Steven Miller in the ''Jago & Litefoot'' audio drama "The Monstrous Menagerie" (2014) *Eamon Stocks in the video game ''Assassin's Creed Syndicate'' (2015) *Ryōhei Kimura, Ryohei Kimura in the mobile game ''Ikémen Vampire: Temptation in the Dark'' (2019)In fiction
Arthur Conan Doyle is the ostensible narrator of Ian Madden's short story "Cracks in an Edifice of Sheer Reason". Sir Arthur Conan Doyle features as a recurring character in Pip Murphy's Christie and Agatha's Detective Agency series, including ''A Discovery Disappears'' and ''Of Mountains and Motors''.See also
* William Gillette, a personal friend who performed the most famous stage version of ''Sherlock Holmes (play), Sherlock Holmes'' * List of Freemasons, List of notable Freemasons * Physician writer#19th century, Physician writerReferences
Further reading
* Martin Booth (2000). ''The Doctor and the Detective: A Biography of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle''. Minotaur Books. * John Dickson Carr (2003 edition, originally published in 1949). ''The Life of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle''. Carroll and Graf Publishers. * Michael Dirda (2014). ''On Conan Doyle: or, The Whole Art of Storytelling''. Princeton University Press. * Arthur Conan Doyle, Joseph McCabe (1920)''Debate on Spiritualism: Between Arthur Conan Doyle and Joseph McCabe''
The Appeal's Pocket Series. * Bernard M. L. Ernst, Hereward Carrington (1932). ''Houdini and Conan Doyle: The Story of a Strange Friendship''. Albert and Charles Boni, Inc. * Margalit Fox (2018). ''Conan Doyle for the Defense''. Random House. * Kelvin Jones (1989). ''Conan Doyle and the Spirits: The Spiritualist Career of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle''. Aquarian Press. * Jon Lellenberg, Daniel Stashower, Charles Foley (2007). ''Arthur Conan Doyle: A Life in Letters''. HarperPress. * Andrew Lycett (2008). ''The Man Who Created Sherlock Holmes: The Life and Times of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle''. Free Press. * Russell Miller (2008). ''The Adventures of Arthur Conan Doyle: A Biography''. Thomas Dunne Books. * Pierre Nordon (1967). ''Conan Doyle: A Biography''. Holt, Rinehart and Winston. * Ronald Pearsall (1977). ''Conan Doyle: A Biographical Solution''. Littlehampton Book Services Ltd. * Massimo Polidoro (2001). ''Final Séance: The Strange Friendship Between Houdini and Conan Doyle''. Prometheus Books. * Daniel Stashower (2000). ''Teller of Tales: The Life of Arthur Conan Doyle''. Penguin Books.
External links
Digital collections * * *Works by Arthur Conan Doyle
at Project Gutenberg Australia * *
Poems by Arthur Conan Doyle
Physical collections
Arthur Conan Doyle Papers
an
Personal Effects
at the Harry Ransom Center
Arthur Conan Doyle Collection
at Toronto Public Library
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle Collection
at Dartmouth College Library
*
at the Newberry Library * Biographical information
Doyle, Sir Arthur Conan, Knt. – Cr. 1902
''The county families of the United Kingdom'' or ''Royal manual of the titled and untitled aristocracy of England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland'', (Volume ed. 59, yr. 1919) (page 109 of 415) by Edward Walford
The Arthur Conan Doyle Encyclopedia
Conan Doyle in Birmingham
Other references
1930 audio recording of Conan Doyle speaking
* *
Arthur Conan Doyle quotes
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Doyle, Arthur Conan Arthur Conan Doyle, 1859 births 1930 deaths 19th-century British novelists 19th-century British short story writers 19th-century Scottish medical doctors 19th-century Scottish writers 19th-century male writers 20th-century British male writers 20th-century British novelists 20th-century Scottish medical doctors Alumni of the University of Edinburgh Association footballers not categorized by position British Freemasons British male boxers British children's writers British crime fiction writers British detective fiction writers British dramatists and playwrights British essayists British fantasy writers British historical novelists British horror writers British male novelists British male poets British memoirists British mystery writers British non-fiction writers British occult writers British opera librettists British people in whaling British people of Irish descent British science fiction writers British short story writers British spiritualists Deputy Lieutenants of Surrey Doyle family, Arthur Conan English footballers Former Roman Catholics Ghost story writers Knights Bachelor Knights of Grace of the Order of St John Legion of Frontiersmen members Liberal Unionist Party parliamentary candidates Male non-fiction writers Maritime writers Marylebone Cricket Club cricketers Mythopoeic writers People educated at Stonyhurst College People of the Second Boer War Recipients of the Order of the Crown (Italy) Scottish Christian mystics Scottish cricketers Sherlock Holmes Victorian novelists Writers from Edinburgh Writers of Gothic fiction Writers of historical fiction set in the Middle Ages Writers of historical fiction set in the modern age People of the National Rifle Association